
Low Latent Inhibition YouTube
Modeling Schizophrenia in Animals. David Feifel, Paul D. Shilling, in Animal Models for the Study of Human Disease, 2013. Latent Inhibition. Latent inhibition is a normal modulation of associative learning. Specifically, latent inhibition refers to the reduced ability to learn the relevance of a stimulus that is paired with an aversive or positive condition through classic conditioning if.

Cumulative survival for the low UnEx group in the auditory latent... Download Scientific Diagram
Low-latent inhibition (LLI) is not a stick illness or syndrome rather it's a behavioral term that has different causes that depend on one's IQ. A person being affected, having a high IQ is in.

Low Latent Inhibition and the Qur'ān with Dr. Abdulla Galadari YouTube
Latent inhibition (LI) is a startlingly simple effect in which preexposure of a stimulus without consequence retards subsequent responding to a stimulus-consequence relation.. Latent inhibition in low and high "psychotic-prone" normal subjects. Personality and Individual Differences. 1992; 13 (5):563-572. [Google Scholar] Lubow RE.

Behavioral results from latent inhibition with extended preexposure in... Download Scientific
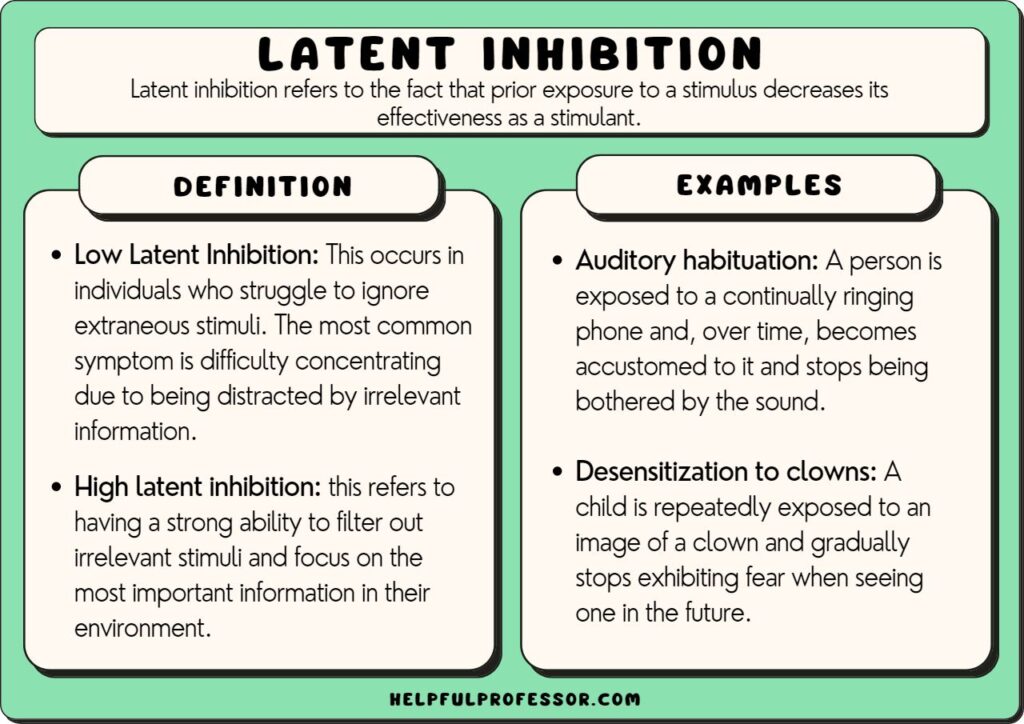
Latent inhibition (LI) is a technical term in classical conditioning, where a familiar stimulus takes longer to acquire meaning (as a signal or conditioned stimulus) than a new stimulus. [1] The term originated with Lubow and Moore in 1973. [2]

Low Latent Inhibition YouTube
Low latent inhibition is not an ideal state.Wikipedia lists several potential problems including attentional and emotional dysregulation, psychosis, and negative emotionality. Wikipedia also suggests that intelligence may moderate effects on well-being, such that more highly intelligent people could cope with stronger stimulation more.

ميگن فيلما رو با دقت ببيني چيز جديد ياد ميگيري همينجاس! low latent inhibition prison break
Latent inhibition is a phenomenon which refers to a retardation in learning about a stimulus that has been rendered irrelevant by mere non-reinforced preexposure, compared to a non-preexposed stimulus, during a subsequent test of learning [ 1 ].

LOW LATENT INHIBITION? An in depth look at the pros and cons I Bipolar Barbie YouTube
Latent inhibition is a term used to explain how our observation of a familiar stimulus (e.g. something we see, hear, smell, feel or taste that we've had before) takes longer to acquire meaning than a new stimulus. It's essentially a mental tool you develop in order to experience the world in a manageable way.

Latent Inhibition Conditioned by Robert E. Lubow (English) Hardcover Book Free S 9780521363075
Creative people and low levels of latent inhibition A University of Toronto press release on the study explained, "Other people's brains might shut out this same information through a process called 'latent inhibition' - defined as an animal's unconscious capacity to ignore stimuli that experience has shown are irrelevant to its needs.

Modulation of the Latent Inhibition (LI) Effect by Periadolescent... Download Scientific Diagram
Latent inhibition (LI) is the reduced efficacy of a previously exposed, inconsequential stimulus to generate a conditioned response when paired with reinforcement, compared with a novel stimulus.. Amphetamine- and low scopolamine-induced disrupted LI, although reflecting distinct psychological processes, are reversed by both typical and.

Individual learning phenotypes drive collective behavior PNAS
Request Appointment LATENT INHIBITION: FILTERING OUT THE MADNESS? Hope Mental Health Blog LATENT INHIBITION: FILTERING OUT THE MADNESS? Tweet I've written here before about a link between creativity and madness-artistic individuals are much more likely than non-artistic individuals to have a genetic predisposition toward mental illness.

Low Latent Inhibition Benefits and Downsides YouTube
Carson et al. (2003), psychologists and investigators from Toronto and Harvard University, identified low latent inhibition as one of the biological foundations of creativity, stating that the creative people's brains are in contact with more of the environmental stimulus than non-creative ones, since the process of information does not stop.

Context sensitivity of latent inhibition when the conditioned stimulus... Download Scientific
With low latent inhibition, an individual can almost treat familiar stimuli in the same manner as they would new stimuli. Think of the details you notice when you see something new for the first time and how it grabs your attention. From that all kinds of questions may arise in your mind. "What is that, what does it do, why is it there, what.

The behavioral results for learned irrelevance and latent inhibition... Download Scientific
Current works about low latent inhibition reinforce the idea of problem-finding as the source of problem-solving (Runco, 1994). When more information enters, the higher the probability is of a combination, which will then generate new ideas. In summary, the amount of information that an individual can manage is directly linked to the creation.

LLI Episode 1 Introduction YouTube
Latent inhibition is the psychological phenomenon where exposure to a stimulus that has no consequence makes it harder to learn new associations with that stimulus later on. In simpler terms, if you've ignored something as irrelevant before, you're less likely to notice or learn from it in the future.

» What is Low Latent Inhibition Educational tools, Infj famous, Low
Latent inhibition is a psychological phenomenon whereby the prior experience of a stimulus reduces its effectiveness as a motivator in subsequent encounters. According to Byrom and colleagues (2018),
Latent Inhibition 10 Examples and Definition (2023)
Latent inhibition (LI) is a robust phenomenon in which repeated preexposure to a stimulus that is not reinforced retards future associability to that stimulus (Lubow,1989).. Latent inhibition in low and high "psychotic-prone" normal subjects. Personality and Individual Differences, 13, 563-572.